Deferred Payments: An In-Depth Overview

- What is a Deferred Payment?
- How Deferred Payment Agreements Work
- 2 Types of Deferred Payments
- 1. Personal Loan Deferments
- 2. Business Loan Deferments
- 3 Examples of Deferred Payments
- 1. Car Loans
- 2. Student Loans
- 3. Mortgage Loans
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Deferred Payments
- 3 Advantages
- 3 Disadvantages
- How to Qualify for Deferred Payments:
- Best 5 Practices for Managing Deferred Payments
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations
- Conclusion
Imagine you’re eyeing that shiny new gadget or dreaming about upgrading your business equipment, but your wallet isn’t quite ready to make it happen just yet.
Deferred payments swoop in like a financial superhero, letting you snag what you need now and worry about the payment later.
It's like having your cake and eating it too, without the immediate calorie count!
Whether you’re an individual managing personal expenses or a business navigating cash flow hiccups, deferred payments can provide the breathing room you need to keep things running smoothly.
Dive into this guide to uncover how deferred payments can work wonders for your financial strategy.
What is a Deferred Payment?
A deferred payment is a financial arrangement where the payment for a purchase or a loan is delayed until a future date.
This arrangement allows borrowers to make expensive purchases without paying the full amount upfront, spreading the cost over a specified period.
Deferred payments can be applied to various types of loans and purchases, making them a flexible financial tool for both individuals and businesses.
How Deferred Payment Agreements Work
Each deferred payment plan is tailored to the specifics of the transaction and the agreement between the lender and the borrower.
Typically, the borrower agrees to make payments at a later date, either in one lump sum or in installments. The terms of the deferred payment, including the amount to be paid, the schedule of payments, and any applicable interest or fees, are outlined in the agreement.
For example, a piece of equipment costing $10,000 might be paid off over five months with monthly payments of $2,000.
In some cases, the borrower might be allowed to skip the first month's payment or pay a reduced amount initially, followed by regular installment payments thereafter.
This flexibility makes deferred payments an attractive option for managing large expenses.
2 Types of Deferred Payments
1. Personal Loan Deferments
Personal loan deferments are agreements where payments on a personal loan are postponed for a specified period. These deferments are often used during times of financial hardship, such as job loss, illness, or other personal emergencies.
The deferment period can last from one month to a year, depending on the lender's policies and the borrower's financial situation.
To qualify for a personal loan deferment, borrowers typically need to demonstrate their financial hardship and provide supporting documentation.
The approval process may also consider factors such as the borrower's credit history, the type of loan, and the lender's specific policies.
2. Business Loan Deferments
Business loan deferments are arrangements that allow businesses to pause loan payments due to extraordinary circumstances. These deferments can be critical for businesses facing temporary financial difficulties, such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or other unexpected events.
For example, after Hurricane Katrina, the Small Business Administration (SBA) offered four-year deferments to affected businesses, allowing them time to recover without the immediate burden of loan payments.
Business loan deferments can vary in length and terms, depending on the lender and the specific situation. Some banks may offer short-term deferments of one to three months for businesses experiencing cash flow problems, while others may provide longer-term solutions for more severe disruptions.
If you want to always have your finances under control, we recommend you use a corporate cash flow management software. This tool can help you to effortlessly categorize expenses, set spending limits, and generate customizable reports to gain insights into your spending patterns.
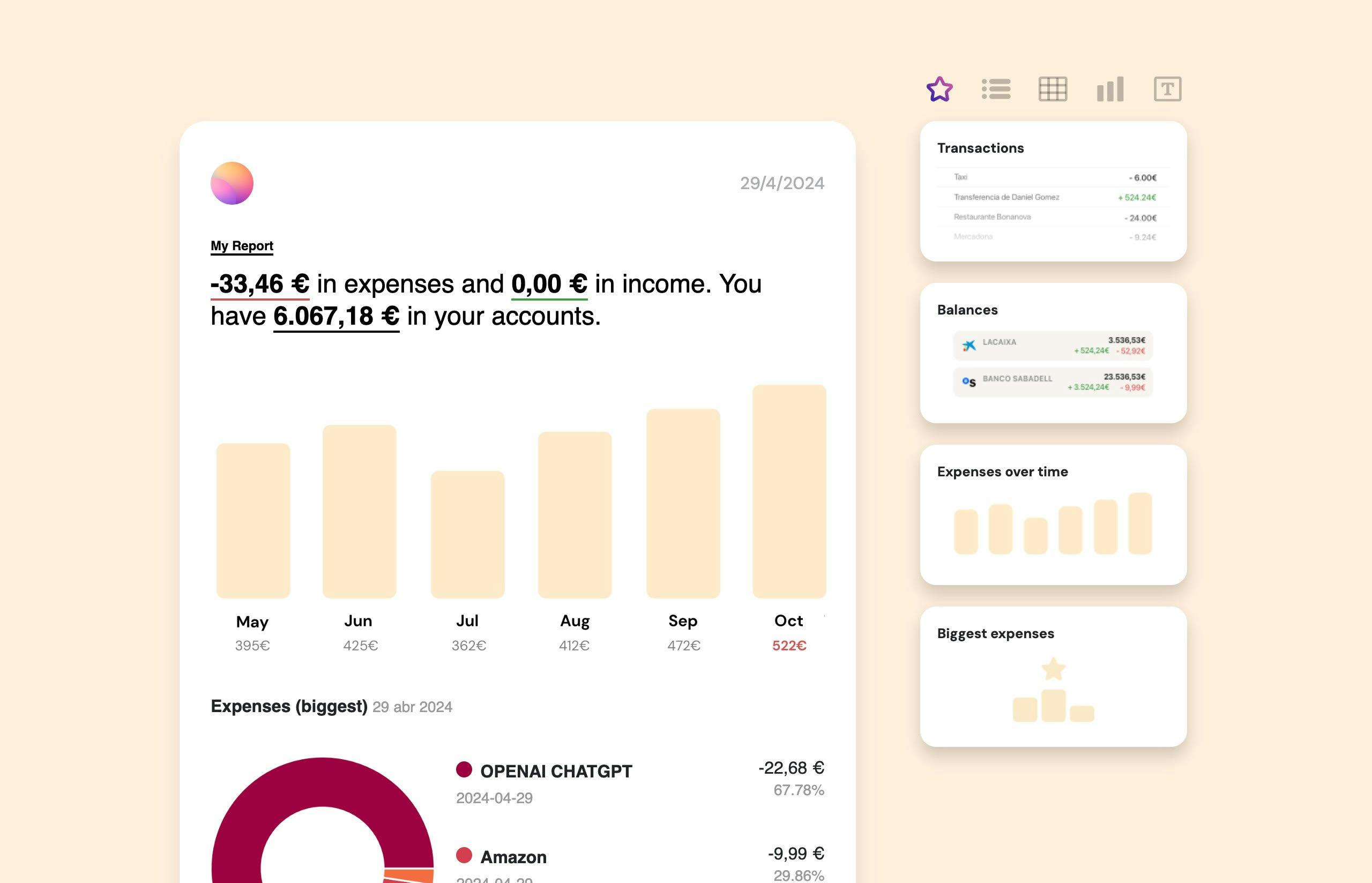
The key to obtaining a business loan deferment is demonstrating the temporary nature of the financial hardship and presenting a viable plan for returning to regular payments once the deferment period ends.
3 Examples of Deferred Payments
Deferred payments are common in various scenarios, including car loans, student loans, and mortgage loans.
Each type of deferred payment arrangement has its own unique characteristics and benefits.
1. Car Loans
Deferred payments on car loans are often used to make vehicle purchases more affordable.
During times of economic hardship, car manufacturers and dealerships may offer deferred payment programs to attract customers.
For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, Hyundai introduced a deferred payment program that allowed customers to defer payments for up to three months if they experienced job loss or medical hardships.
2. Student Loans
Student loan deferments are a lifeline for many college graduates who face financial challenges after completing their education.
These deferments allow borrowers to temporarily pause payments on their student loans, providing relief during periods of unemployment or underemployment.
However, it's important to note that interest may continue to accrue on the deferred loans, increasing the overall repayment amount.
3. Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loan deferments can help homeowners avoid foreclosure during financial difficulties. These deferments temporarily suspend mortgage payments, giving homeowners time to stabilize their finances.
Mortgage deferments were widely used during the COVID-19 pandemic, with many lenders offering relief programs to help borrowers manage their housing costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Deferred Payments
3 Advantages
- Affordability: Deferred payments make large purchases more affordable by spreading out the cost over time. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals and businesses facing temporary financial hardships.
- Cash Flow Management: Deferred payments help manage cash flow by delaying immediate financial obligations. This can provide breathing room for borrowers to handle other expenses.
- Flexibility: Deferred payment arrangements can be customized to fit the borrower's financial situation, making them a flexible option for managing large expenses.
3 Disadvantages
- Interest Costs: Interest can accumulate during the deferment period, increasing the overall cost of the loan or purchase. Borrowers need to consider the long-term financial impact of deferred payments.
- Risk of Default: Borrowers might overestimate their ability to repay the deferred payments, leading to financial trouble if they cannot meet the obligations. This risk underscores the importance of careful financial planning and realistic assessment of one's ability to make future payments.
- Temporary Solution: Deferred payments are often a temporary solution to financial challenges. They do not address underlying financial issues, which may require more comprehensive financial planning and management.
How to Qualify for Deferred Payments:
Qualifying for deferred payments typically involves meeting specific criteria set by the lender.
Here are some common steps and considerations for qualifying for deferred payment arrangements:
- Demonstrate Financial Hardship: Borrowers usually need to demonstrate that they are facing financial hardship, such as job loss, medical emergencies, or natural disasters. Providing documentation, such as income statements, medical bills, or proof of job loss, can support the application.
- Review Lender Policies: Different lenders have different policies regarding deferred payments. It's essential to review the lender's requirements and procedures to understand the eligibility criteria and application process.
- Maintain Good Credit History: A good credit history can improve the chances of qualifying for deferred payments. Borrowers with a history of timely payments are often viewed more favorably by lenders.
- Submit a Formal Request: Borrowers need to submit a formal request for deferred payments, detailing their financial situation and the reasons for the request. This request may include a proposed repayment plan and supporting documentation.
Best 5 Practices for Managing Deferred Payments
Managing deferred payments effectively requires careful planning and proactive financial management. Here are some best practices for managing deferred payments:
- Communicate with Lenders: Maintaining open communication with lenders is crucial. Borrowers should inform lenders of any changes in their financial situation and work together to find suitable solutions.
- Create a Budget: Developing a budget can help borrowers manage their finances during the deferment period. A budget tracking app can provide a clear picture of income, expenses, and savings, helping borrowers make informed financial decisions.
- Plan for Future Payments: Borrowers should plan for the resumption of payments once the deferment period ends. Setting aside funds for future payments can help avoid financial strain when regular payments resume.
- Monitor Interest Accrual: It's important to monitor interest accrual during the deferment period. Borrowers should be aware of how much interest is accumulating and factor this into their repayment plans.
- Seek Financial Advice: Consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and guidance on managing deferred payments and overall financial health.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Deferred payment agreements are subject to various legal and regulatory considerations, depending on the type of loan and jurisdiction.
Here are some key legal and regulatory aspects to consider:
- Consumer Protection Laws: Many jurisdictions have consumer protection laws that regulate deferred payment agreements. These laws are designed to protect borrowers from unfair practices and ensure transparency in lending.
- Loan Agreement Terms: The terms of the loan agreement, including the deferment provisions, should be clearly outlined and agreed upon by both parties. Borrowers should carefully review the terms and seek legal advice if necessary.
- Interest Rate Regulations: Interest rates on deferred payments may be subject to regulatory caps or limits. It's important to understand these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid excessive interest charges.
- Disclosure Requirements: Lenders are often required to disclose all relevant information about the deferred payment agreement, including interest rates, fees, and repayment terms. Borrowers should ensure they receive and understand these disclosures.
Conclusion
Deferred payments provide a flexible and supportive financial solution for both individuals and businesses facing temporary financial challenges. By spreading the cost of large purchases or loans over time, deferred payments help manage cash flow and provide relief during difficult periods.
However, it's important to carefully consider the long-term financial impact and plan accordingly to avoid potential pitfalls.
Borrowers should communicate openly with lenders, develop a realistic budget, and seek financial advice to manage deferred payments effectively.
Understanding the legal and regulatory considerations can also help ensure compliance and protect against unfair practices. With careful planning and proactive management, deferred payments can be a valuable tool for maintaining financial stability and achieving long-term financial goals.
Share this post
Related Posts
Verifactu for Startups in Spain: Complete Guide 2025
Verifactu introduces a new era of electronic invoicing in Spain, requiring startups to send invoices directly to the Tax Agency.Best 7 Cash Flow Management Tools in Finland for 2025
These are the best cash flow management tools in Finland: Banktrack Procountor Netvisor Visma eAccounting Fennoa Float QuickBooks Online In Finland’s competitive business environment, from Helsinki’sHow to track your business cash flow: complete guide
Failing to track cash flow properly can lead to serious financial issues. In this article, we provide efficient solutions to manage and optimize it effectively.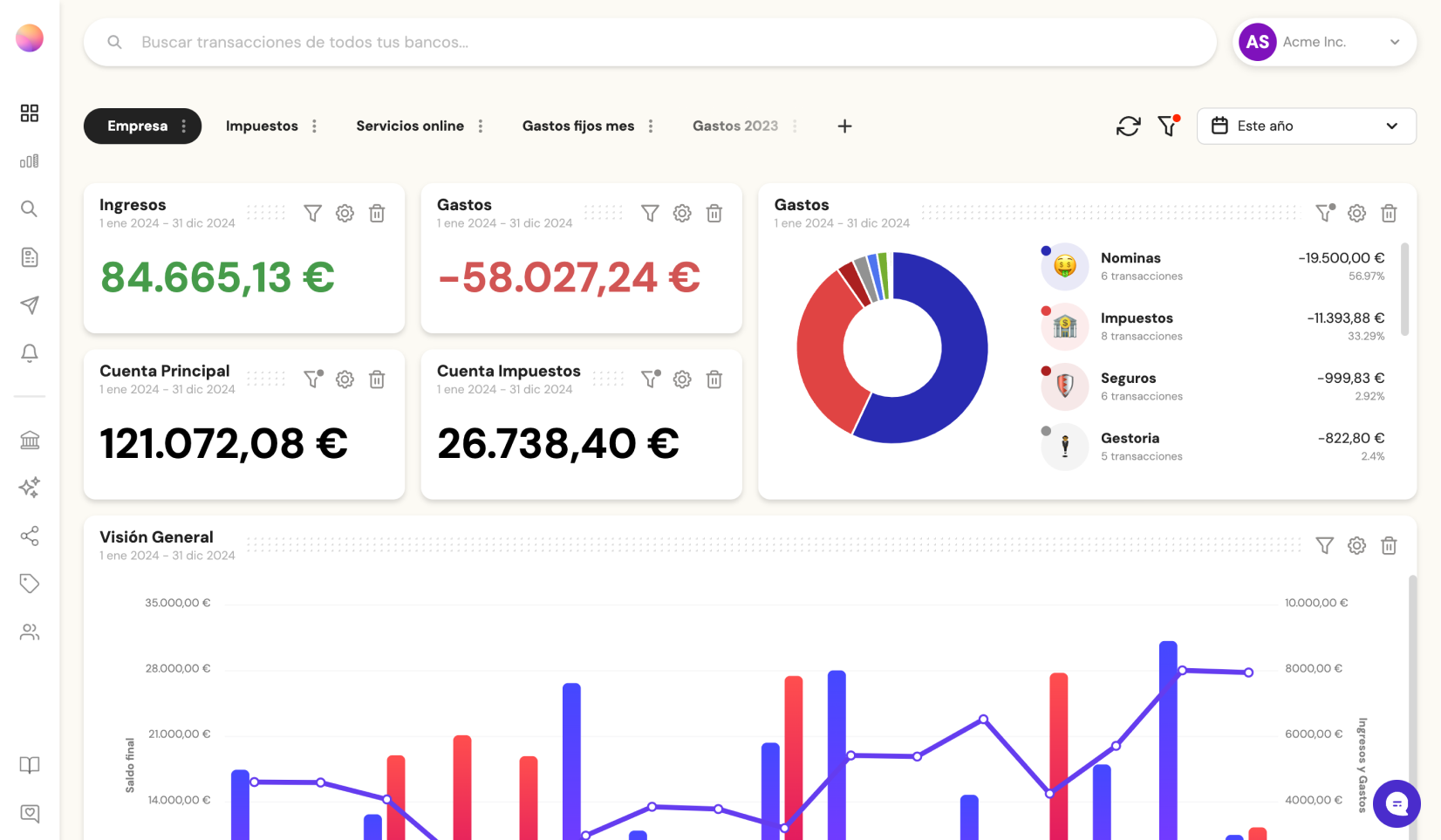
Try it now with your data
- Your free account in 2 minutes
- No credit card needed